Can Taking Melatonin Supplements Disrupt Your Body's Own Melatonin Production?
The eternal question with a straightforward answer.
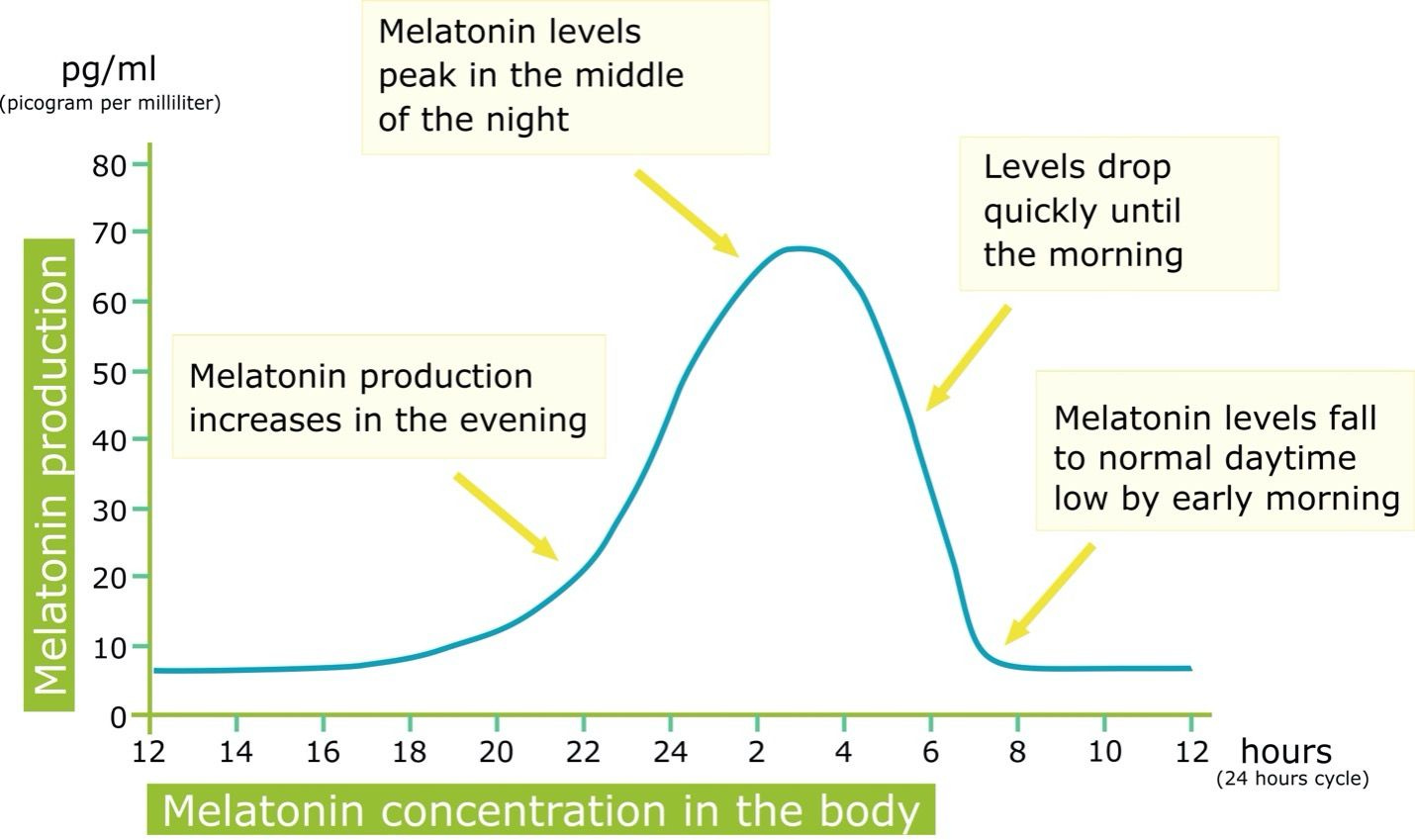
Melatonin is a hormone produced naturally by the pineal gland in the brain that helps regulate the circadian rhythm and sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin levels rise in the evening as it gets darker, making us feel drowsy and helping initiate sleep. They then drop in the morning as light exposure inhibits further melatonin release. Melatonin supplements (1-10mg) are widely used (1 in 3 adults who experience sleep problems) to help improve sleep quality and treat insomnia, but there is come concern whether taking melatonin supplements can inhibit the body's own melatonin production. So what does science have to say about this?
The short answer is: taking melatonin supplements does not suppress your endogenous melatonin secretion. A few older studies from 20+ years ago that studied this reported exogenous melatonin does not suppress endogenous melatonin production. One relatively newer study also concluded the same by giving adults 0.5mg of melatonin for 7 days and 50mg (very high) for 37 days. Some studies even went for longer, up to a year, and showed no decline in endogenous melatonin secretion (1).
Figure 1. The normal daily cycle of melatonin.
So what can lower your melatonin? Age is one of the most common factors, as melatonin production naturally declines as we get older. One study found that melatonin levels peak between 2-5 years of age and then start to decrease over time, as the growth of the pineal gland that secretes it peaks around the age of 1. Certain medical conditions like depression, dementia, and insomnia can also result in insufficient endogenous melatonin production or secretion. This is why people with these conditions may benefit more from melatonin supplementation since their natural melatonin levels are already lowered. Maintaining healthy sleep routines in general is important for robust endogenous melatonin release at night.
In conclusion, while melatonin supplements have become widely popular for sleep problems, current evidence indicates they do not suppress the body's own ability to produce melatonin at physiological doses and durations. However, maintaining healthy sleep habits remains, as always, important.
(1) https://inpharmd.com/does-supplemental-melatonin-suppress-endogenous-melatonin-production